7.3.7 Water and Electricity Cogeneration
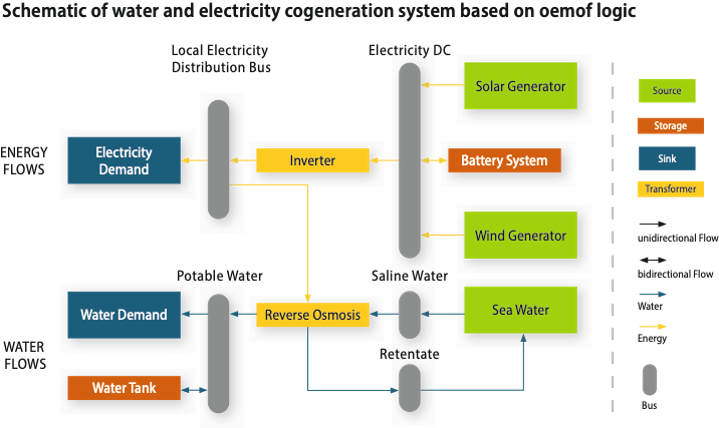
Additional water-energy nexus synergies can be tapped when combining water and energy production in one system. For example, this can be reached via multistage solar photovoltaic membrane distillation (Wang et al., 2019) or photovoltaic-battery-reverse osmosis systems (Zein et al. 2018). A comparable system is visualized in the section applying an energy system modeling logic (oemof, Hilpert 2018). The reverse osmosis unit acts as a flexible load (demand-side management) and the water tank as indirect energy storage). Thereby, the components increase the energy uptake from the fluctuating solar energy resource and thus the overall (cost) efficiency of the system.
References Hilpert S, Kaldemeyer C, Krien U, Günther S, Wingenbach C, Plessmann G (2018) The Open Energy Modelling Framework (oemof) - A new approach to facilitate open science in energy system modelling. Energy Strategy Reviews 22:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esr.2018.07.001
Oemof. Open Energy Modelling Framework - A modular open energy framework to model energy supply systems. Available online: https://github.com/oemof (last check on 11/04/2020)
Wang W, Shi Y, Zhang C, Hong S, Le Shi, Chang J, Li R, Jin Y, Ong C, Zhuo S, Wang P (2019) Simultaneous production of fresh water and electricity via multistage solar phoOovoltaic membrane distillation. Nature Communications 10:3012. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10817-6
Zein A, Ghabech C, Karaki SH (2018) Optimization of a Solar Photovoltaic Micro Grid for Electricity and Desalinated Water Production. In: 2018 4th International Conference on Renewable Energies for Developing Countries (REDEC): 1-2 Nov. 2018. IEEE, Piscataway, NJ, pp 1–6.
Figure drawn by using draw.io app. Available online; https://app.diagrams.net/